Planting Your North Florida Backyard: A Complete Vegetable Calendar
Planting Your North Florida Backyard: A Complete Vegetable Calendar
Associated Articles: Planting Your North Florida Backyard: A Complete Vegetable Calendar
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Planting Your North Florida Backyard: A Complete Vegetable Calendar. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Planting Your North Florida Backyard: A Complete Vegetable Calendar
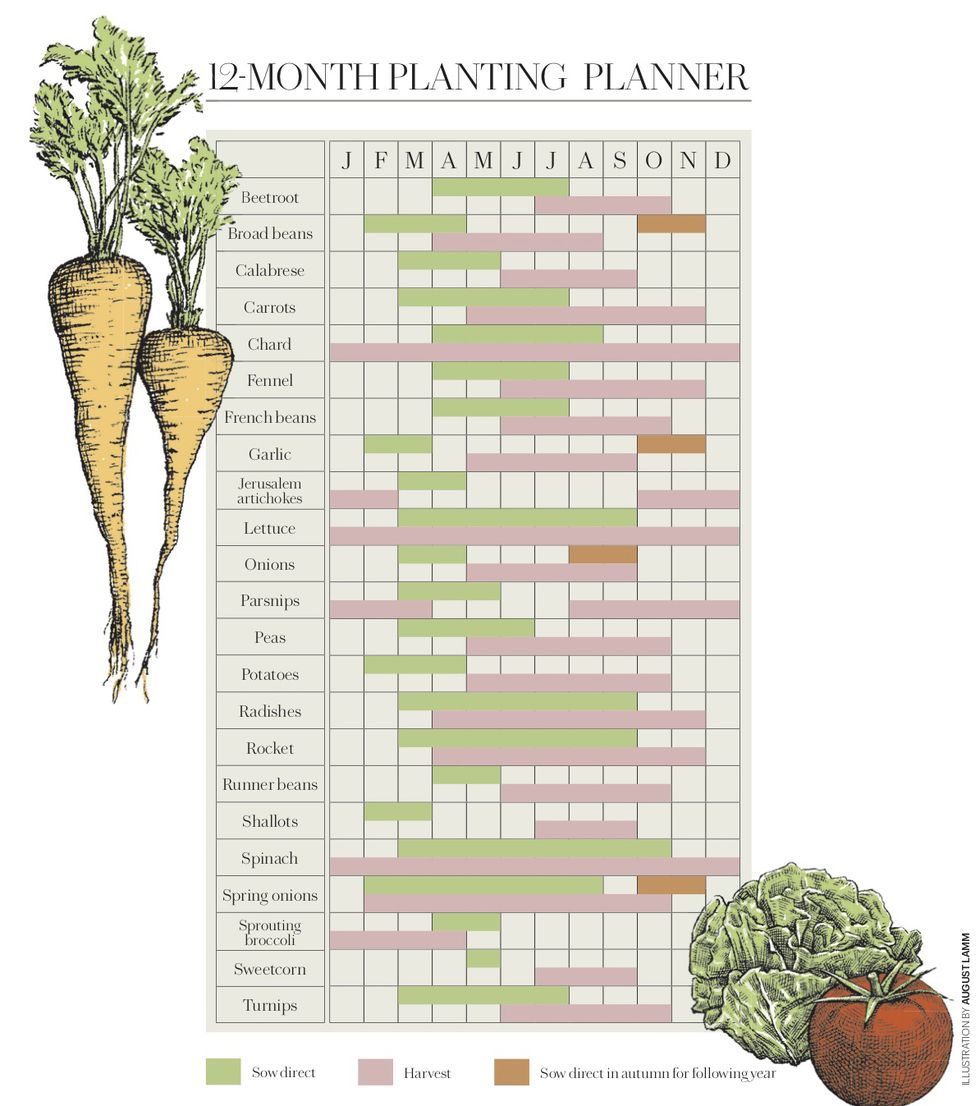
North Florida boasts a protracted rising season, permitting gardeners to domesticate a various array of greens. Nonetheless, understanding the nuances of the area’s local weather is essential for maximizing yields. This detailed planting calendar considers the distinctive challenges and alternatives offered by North Florida’s climate patterns, encompassing the microclimates discovered inside the area. From the milder coastal areas to the marginally cooler inland areas, this information gives tailor-made recommendation for profitable vegetable gardening.
Understanding North Florida’s Local weather:
North Florida’s local weather is characterised by scorching, humid summers and gentle, comparatively brief winters. Frost is a priority, notably within the northernmost components of the area and at larger elevations. The typical final frost date varies considerably, starting from late February to early March within the southern components to late March and even early April within the northern areas. The primary frost sometimes arrives in late October or early November. This dictates the planting schedule for a lot of cool-season and warm-season crops. Rainfall is mostly well-distributed all year long, though summer time months can expertise intervals of intense rainfall and humidity. This humidity can contribute to fungal illnesses, requiring cautious consideration to plant spacing and air circulation.
Cool-Season Greens (Planting in Fall/Winter):
Cool-season greens thrive within the milder temperatures of fall, winter, and early spring. These crops usually choose temperatures between 50-70°F (10-21°C). Planting occasions ought to be adjusted primarily based in your particular location inside North Florida and the anticipated final frost date.
-
September – October: Start sowing seeds or transplanting seedlings of broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, kale, collard greens, lettuce, spinach, and mustard greens. These crops will mature earlier than the primary frost. Think about using row covers or low tunnels to increase their rising season and shield in opposition to early frosts.
-
October – November: Plant hardy types of peas, radishes, turnips, and carrots. These crops can tolerate gentle frosts and can proceed to develop all through the cooler months. For a steady harvest, stagger plantings over a number of weeks.
-
November – December: It is a good time to plant garlic and onions for a spring harvest. These crops require a interval of chilly temperatures to correctly develop bulbs. Plant shallots and scallions as properly.
-
January – February: Proceed planting cool-season crops like spinach, lettuce, and radishes. These will be efficiently grown in protected areas, even throughout gentle freezes. Think about using chilly frames or different protecting buildings to increase the rising season.
Heat-Season Greens (Planting in Spring/Summer time):
Heat-season greens want constantly heat temperatures and loads of sunshine to thrive. These crops usually choose temperatures above 65°F (18°C).
-
March – April: As the chance of frost diminishes, start planting warm-season crops similar to tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, squash (summer time and zucchini), cucumbers, and beans (bush and pole). Begin seeds indoors 4-6 weeks earlier than the final frost date for a head begin. Direct sowing can be an choice for a few of these crops.
-
April – Might: This is a perfect time to plant corn, melons (watermelon, cantaloupe, honeydew), and okra. These crops require lengthy, heat rising seasons to provide plentiful yields. Guarantee correct spacing to permit for ample air circulation and forestall fungal illnesses.
-
Might – June: Plant heat-tolerant types of beans, squash, and cucumbers. Proceed succession planting of quick-maturing crops like beans and zucchini to take care of a steady harvest all through the summer time.
-
June – July: Contemplate planting heat-tolerant greens, similar to Southern peas (black-eyed peas, crowder peas) and okra. Be aware of the elevated humidity and potential for pest issues throughout this era.
Succession Planting:
Succession planting is essential for maximizing yields and having fun with a steady harvest all through the rising season. This entails planting small batches of fast-growing crops at common intervals, making certain a relentless provide of recent greens. Examples embody:
- Lettuce: Plant each 2-3 weeks for a steady provide of recent leaves.
- Radishes: A fast-growing crop that may be planted each few weeks.
- Bush beans: Plant each 2-3 weeks for a steady harvest.
- Zucchini: Recognized for its speedy progress and prolific manufacturing. Plant a number of vegetation and harvest regularly.
Microclimate Issues:
North Florida’s various geography creates variations in microclimates. Coastal areas usually get pleasure from milder temperatures and better humidity in comparison with inland areas. Larger elevations might expertise barely cooler temperatures and an extended frost season. Contemplate these components when selecting planting dates and choosing plant varieties. South-facing slopes are typically hotter, whereas north-facing slopes are cooler. These variations can affect the timing of planting and the success of sure crops.
Pest and Illness Administration:
North Florida’s humid local weather creates favorable situations for numerous pests and illnesses. Implementing preventative measures is essential for wholesome vegetation. This consists of:
- Crop rotation: Rotating crops yearly helps to interrupt pest and illness cycles.
- Correct spacing: Sufficient spacing between vegetation promotes air circulation and reduces fungal illnesses.
- Mulching: Mulching helps to retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
- Monitoring: Commonly examine vegetation for indicators of pests and illnesses. Early detection and remedy are important.
- Natural pest management: Make the most of natural strategies similar to helpful bugs, neem oil, and insecticidal cleaning soap to handle pests.
Soil Preparation:
Wholesome soil is key to profitable vegetable gardening. Earlier than planting, conduct a soil take a look at to find out its pH and nutrient ranges. Amend the soil with natural matter, similar to compost or well-rotted manure, to enhance drainage, aeration, and nutrient content material. North Florida soils can differ enormously, with some being sandy and others extra clay-like. Modify your soil preparation methods accordingly.
Watering:
Constant watering is essential, notably throughout dry spells. Water deeply and fewer regularly to encourage deep root progress. Use mulch to assist retain soil moisture and cut back the frequency of watering. Overwatering can result in root rot and different issues, so monitor soil moisture fastidiously.
By fastidiously contemplating these components and using this planting calendar as a information, North Florida gardeners can get pleasure from bountiful harvests of recent, homegrown greens all year long. Keep in mind to at all times seek the advice of native sources and adapt your gardening practices to the particular situations of your backyard. Blissful gardening!








Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Planting Your North Florida Backyard: A Complete Vegetable Calendar. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!